Describe the Basis of Signal Amplification and Explain Its Significance
Applications of Transistor as an Amplifier. Hello Meha Amplification basically means increasing the amplitude of the signal without changing its time period or wavelength.
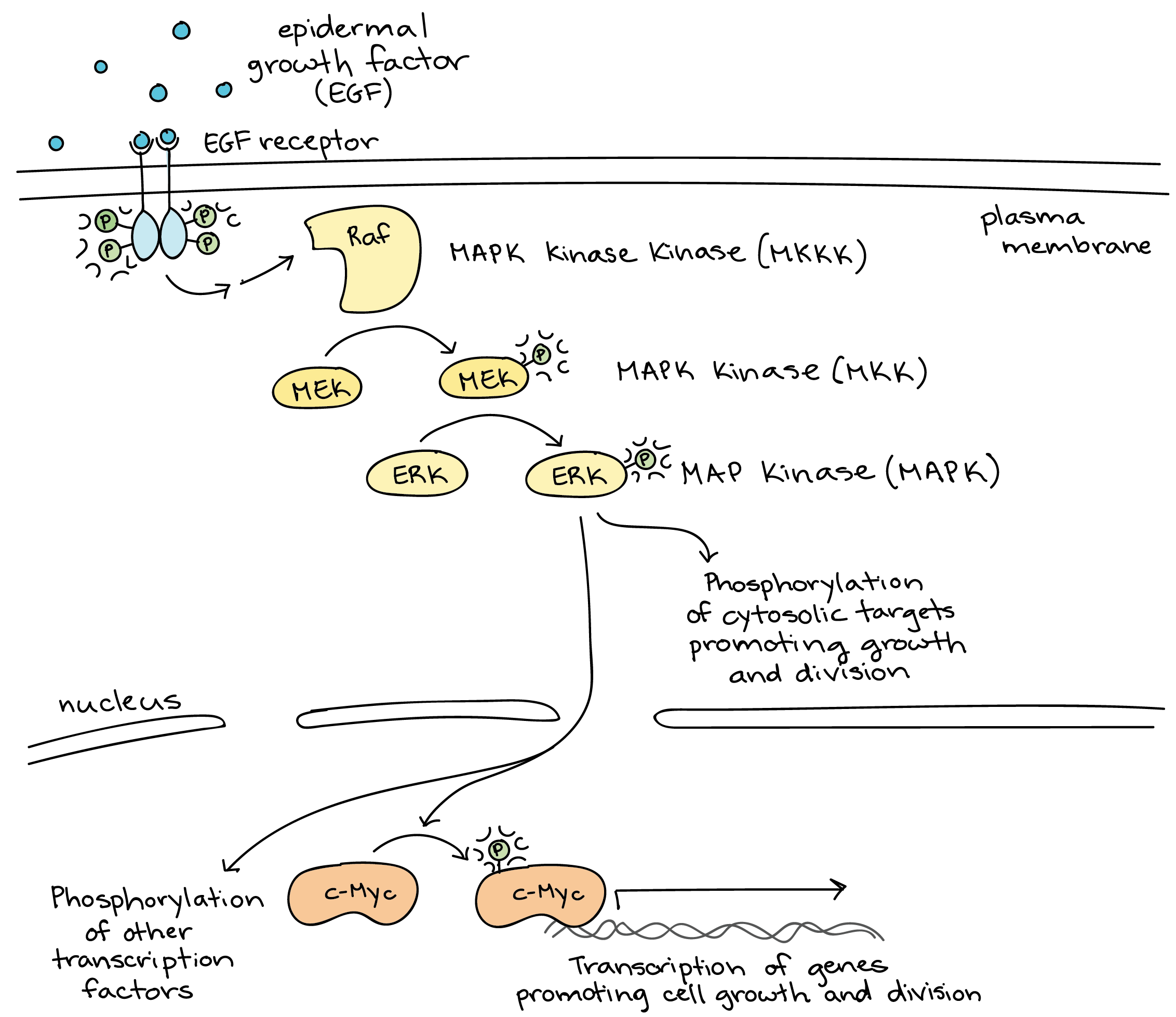
Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
Explain what is meant by antagonistic hormones and examples.
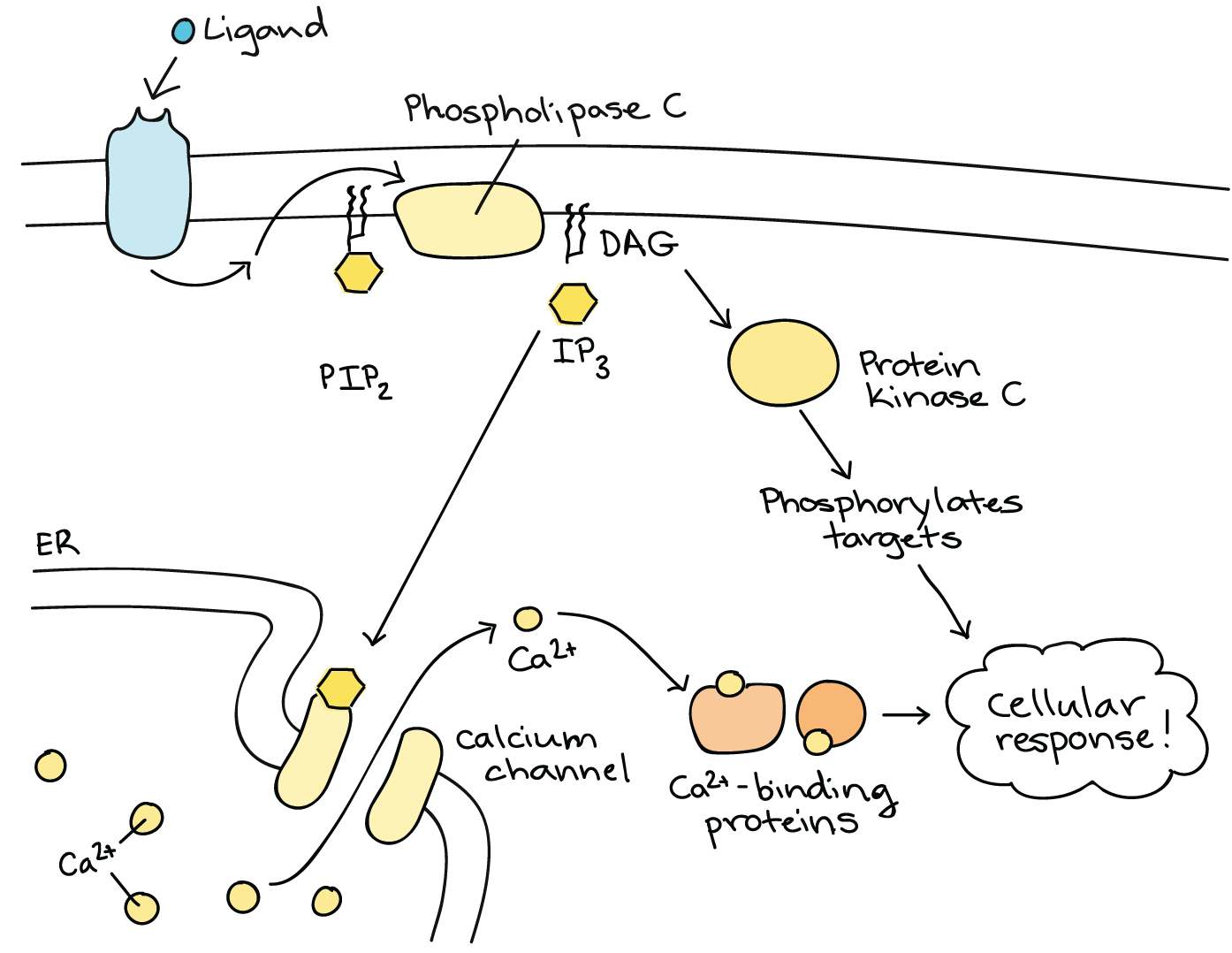
. Amplification is done because when the signal. A signal is said to be continuous when it is defined for all instants of time. What is signal amplification.
Clustering could enable a receptor to amplify ligand-binding signals by imposing its signaling state on its neighbors through conformational spreading Bray et al 1998. Amplitude is the strength or height of the signal waveform. Nucleic acids can be detected using either target or signal amplification methods.
The amplitude of EMG is random in nature. Signal amplification based on nucleic. When a signaling molecule joins with an appropriate receptor on a cell surface this binding triggers.
It also measures the strength of the signal when it returns. The use of specific detection methodologies to directly increase the signal in proportion to the amount of target in the reaction. Explain why athletes should drink solutions that are.
Transistor working as an amplifier has various advantages and applications in the field of electronics and communication. However not all sending and receiving cells are next-door neighbors nor do all cell pairs. Amplification generally results from the activation of a series of enzymatic steps involved in hormone action.
Inherent instability of signal. Signal amplification increases or amplifies the signal generated from the probe molecule hybridized to the target nucleic acid sequence. More precisely it is the ratio of the output signal amplitude to the input signal amplitude and is given the symbol A.
As these functions are orthogonal to each other any two. The number of target molecules per unit volume of sample is a key variable in all biological detection applications. Generally it takes on.
Cell-cell signaling involves the transmission of a signal from a sending cell to a receiving cell. A signal may reach a cell in the form of a single hormone molecule. Binding initiates a signaling pathway.
Orthogonal Signal Space Let us consider a set of n mutually orthogonal functions x 1 t x 2 t. Why a second messenger is needed to convey a signal inside a cell from a water soluble first messanger. Answer 1 of 4.
Briefly target amplification enzymati-cally increases the number of target molecules. EMG signal is affected by the firing rate of the motor units which in most conditions fire in the. Inside the cell the signal must be amplified so that the response is carried out multiple times rather than just by a single.
Elaborate enzyme cascades in each step the cascade the number of activated products is much greater. Although it is possible to control target. It can be calculated for voltage A v current A i or power A p When.
At each step many times more signal molecules are generated. Cells typically receive signals in chemical form via various signaling molecules. When a ligand binds to a cell-surface receptor the receptors intracellular domain part inside the cell changes in some way.
Most cell surface receptors stimulate intracellular target enzymes which may be either directly linked or indirectly coupled to receptors by G proteins. It measures the time it takes for a radio signal of a particular frequency to travel to a target and back. Visually it is the height of the waveform from its centerline or x-axis.
The y-axis of a signals waveform shows the amplitude. The advantages of signal. In electronics signal conditioning is the manipulation of an analog signal in such a way that it meets the requirements of the next stage for further processing.
Ultrasensitive protein assays rely on signal amplification which provides amplified recognition and amplify weak input signals. X n t over the interval t 1 to t 2. A signal is said to be discrete when it is defined at only discrete instants of time Deterministic and Non.

Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
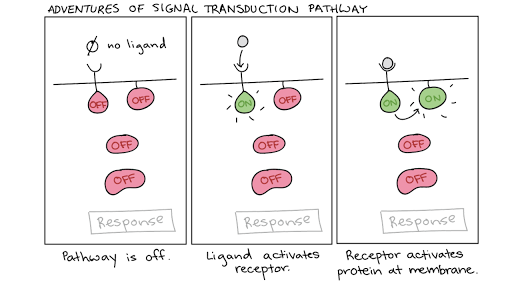
Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
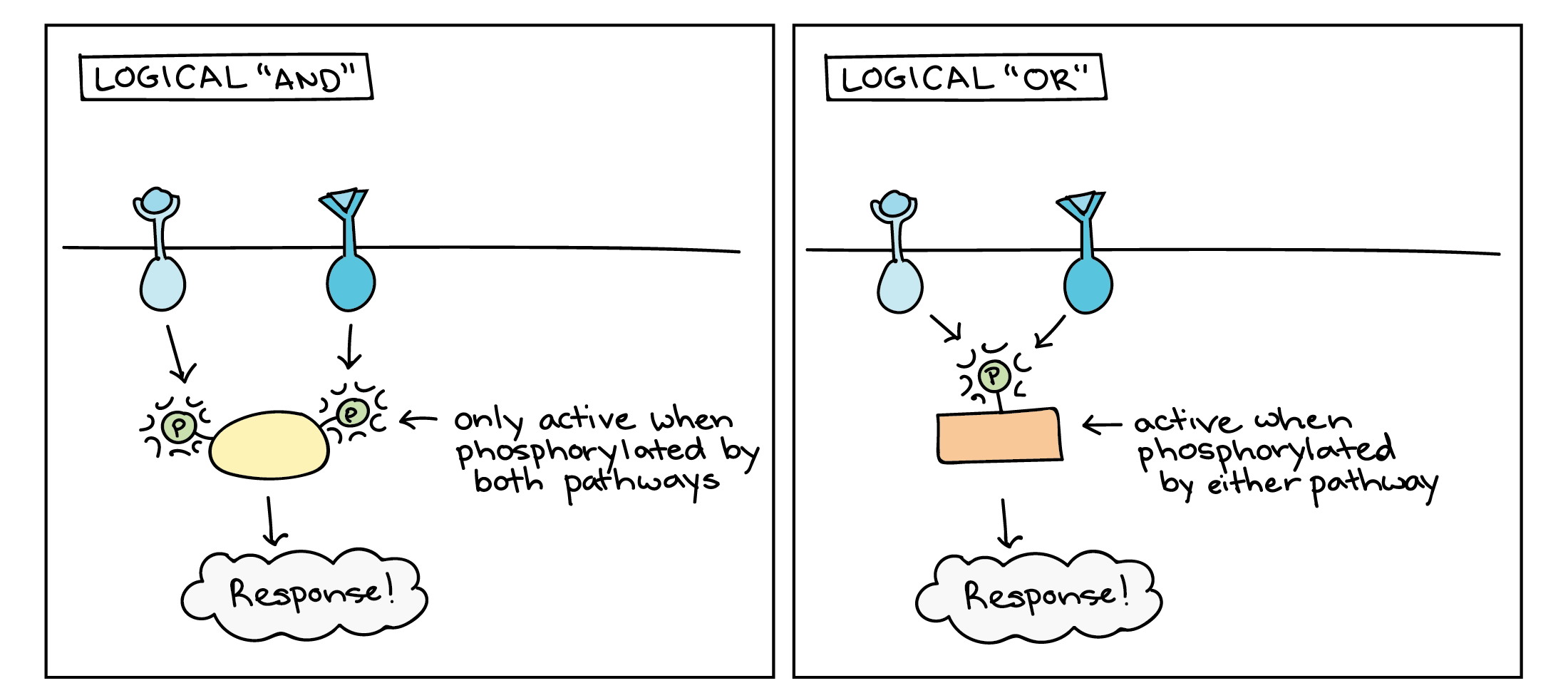
Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
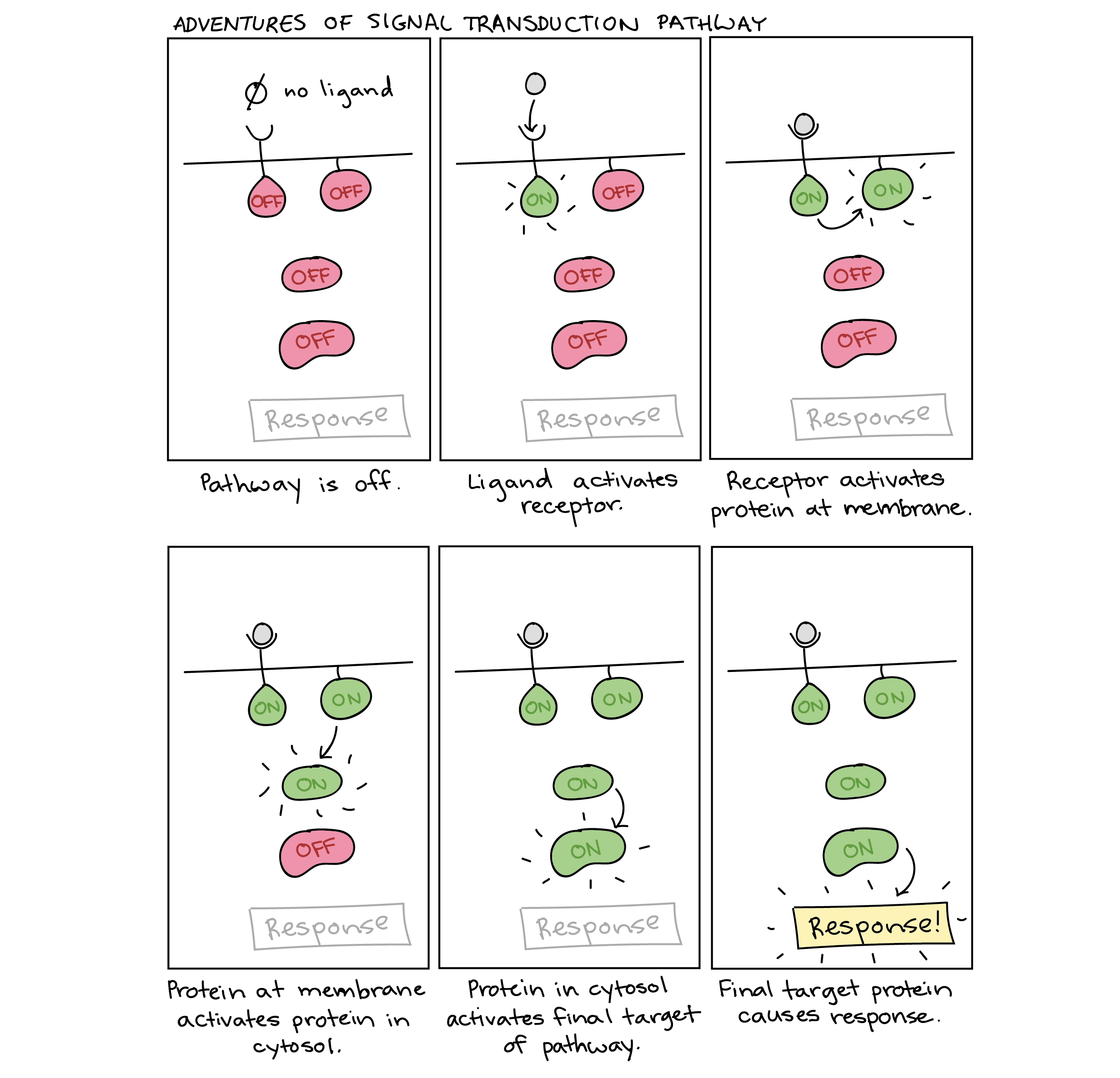
Signal Transduction Pathway Cell Signaling Article Khan Academy
No comments for "Describe the Basis of Signal Amplification and Explain Its Significance"
Post a Comment